The leading companies worked in air conditioning field have prepared their own psychrometric chart. There is slight variation in the charts but overall nature of all the charts are same.
By knowing any two properties state off air can be plotted on the chart and and all of the remaining property can be measured by the chart. It eliminates number of complicated calculations.All the charts are drawn at 760 mm of HG . On x axis dry bulb temperature is taken while on y-axis specific humidity is taken (generally to the the right side of the).
Saturated condition of air at various temperatures are plotted and joining of this all points a smooth curve is obtained. It is known as saturated curve.
On saturated curve dry bulb temperature =weight bulb temperature=Dew Point temperature
Psychrometric chart contains following lines.
1. Dry bulb temperature lines:
This are vertical uniform space lines range from 5 to 45 , sometimes 55.
2. Specific humidity lines:
This are horizontal and equal spacing lines.It Ranges from 0 to 33 gm/kg dry air.
3. Relative humidity lines
These are the curves identical to saturation curve distance between curves increases on right hand side.
4. Wet bulb temperature lines:
These are inclined and non equally spaced lines.
5. Dew Point temperature:
let 1 with state of year Dew Point temperature of this year can be measured by drawing horizontal line up to saturation curve.
Intersection of this line and saturation curve gives Dew Point temperature.
6. Enthalpy lines:
Enthalpy lines are incline lines and extended up to enthalpy screen these lines are coincides with wet bulb temperature lines.
7. Vapour pressure lines:
This are horizontal lines not drawn on main chart but scale showing vapour pressure in mm of HG given on extreme left of the chart.
8. Specific volume lines:
These are inclind line they show volume of dry air in m3/kg(metre cube per kg).
Psychrometric processes:
Various processes are conducted on atmospheric air to change its state to a desired one. These processes are called psychrometric processes.
List of various psychrometric processes:
1. Sensible heating
2. Sensible cooling
3. Humidification
a) heating and humidification
b)cooling and humidification
4. Dehumidification
a) heating with humidification
b) Cooling with humidification
5. Evaporative cooling (cooling with adiabatic humidification )
6. Mixing of two streams
7. Heating and dehumidification of chemical type (chemical dehumidification)
Some basic terms:
Sensible heat:
The heat which causes a change in the temperature is called sensible heat. It is called sensible because it sense by thermometer.
Latent heat:
The heat required to change the phase of substance is called latent heat.during change of phase or state there will be no change in temperature.
amount of heat required to change the liquid into vapour or vice-versa is called latent heat of vaporization. The amount of heat required to change the solid into liquid are liquid into solid is called heat of fusion.
Total heat:
It is the sum of sensible heat and latent heat.
Desirable various Psychrometric processes:
1. Sensible cooling:
cooling of air without any change in its specific humidity is called sensible cooling.
In perfect cooling entering air at temperature T1 will be cooled down to temperature T2, but perfect cooling is not possible in a practice because of loss of cooling effect due to some reason such as conduction,Convection and Bypass hence air leaving will not be called from T1 to T2 but for some higher temperature T3.
Heat rejected= H1 - H3
2. Sensible heating:
Hitting of air without change in its specific humidity is called sensible heating. It is added H3-H1.
3. Humidification and dehumidification:
Addition of moisture to air without change in its a dry bulb temperature is known as humidification.
similarly removal of moisture without change in dry bulb temperature is known as dehumidification.
H2 - H1 does not involving change in temperature but actually practice absolutely modification and humidification is not possible. It is always accompanied by heating or cooling.
 |
| Fig 10.5 Humidifiaction and Dehumidification process |
 |
| Fig 10.6 Heating and humidification |
As shown in the figure spraying hot water in air increases DBT and specific humidity of incoming air .This process is called heating and humidification and it generally used in winter air conditioning.
Total heat added = H3-H1
 |
| Fig 10.7 Heating and humidification on psychrometric chart. |
5. Cooling with Dehumidification:
 |
| Fig 10.8 Cooling with dehumification, |
 |
| Fig 10.9 Cooling with dehumification, |
6. Cooling with adiabetic humidification:
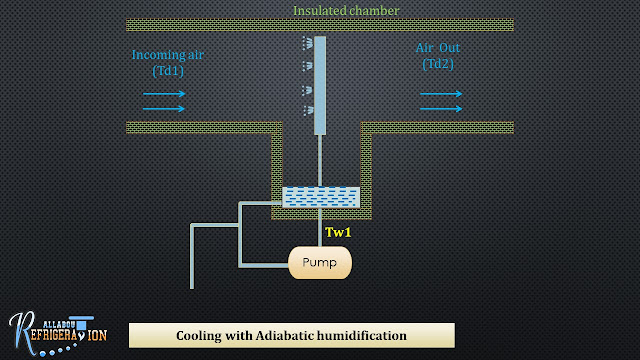 |
| Fig 10.10 Evaporative cooling. |







7 Comments
HVAC mini splits are adaptable with respect to area and are little in stature. They can be utilized to warmth and cool one room, which is perfect in case you're thinking about adding an option to your home.
ReplyDeleteVery well explanation about sensible cooling, Humidification and dehumidification. Thanks for sharing this article
ReplyDeleteI am really happy to say it’s an interesting post to read . I learn new information from your article about Psychrometric chart and processes , you are doing a great job . Keep it up.
ReplyDeleteChina refrigerant gas
ReplyDeleteThanks for sharing this information. The post gives a piece of helpful information about heating and cooling systems. You can also contact B.A.P Heating and Cooling for heating and cooling in Cambridge at an affordable price.
ReplyDeleteNice content it was really great think thanks for sharing
ReplyDeleteBY
Sgaircon aircon service
aircon service
Aircon servicing
aircon servicing Singapore
aircon service Singapore
best aircon service Singapore
best aircon service company
aircon service price
aircon service company Singapore
Nice content
ReplyDeletecaptcha typing job
best captcha typing job
best captcha typing job Daily payment 2024
best transcription services
Best Online Transcription Services for Right Transcripts
How to Get the Most Out of Your Transcription Service